Have you ever wondered why some logistics companies seem to operate like well-oiled machines while others struggle with disconnected systems and data silos? The answer often lies in how effectively they’ve implemented API integrations. In today’s hyperconnected supply chain ecosystem, API integration isn’t just a technical requirement it’s the backbone of efficient logistics operations.
Understanding API Integration in Modern Logistics
What is API Integration in Logistics?
Think of API integration as the universal translator for your logistics technology stack. An Application Programming Interface (API) allows different software systems to communicate with each other seamlessly, exchanging data in real-time without manual intervention.
In logistics, this means your warehouse management system can talk to your transportation management platform, which connects to your customer relationship management software, creating a unified operational ecosystem.
When you’re tracking a shipment from Shanghai to Los Angeles, multiple systems need to exchange information: customs documentation, carrier tracking, inventory updates, and customer notifications. API integration makes this complex dance look effortless, ensuring everyone has the right information at the right time.
Why API Integration Matters for Supply Chain Operations
The logistics industry moves fast literally. Your customers expect real-time visibility, your partners need instant updates, and your team requires accurate data to make split-second decisions. Manual data entry or batch processing simply can’t keep pace with modern expectations.
API integration eliminates data silos, reduces human error, and accelerates information flow across your entire supply chain.
At Cargofive, we’ve seen firsthand how proper API integration can transform a logistics operation from reactive to proactive, turning data into actionable insights that drive better business outcomes.
The Current State of Logistics Technology
Digital Transformation in Freight Management
The logistics landscape has evolved dramatically over the past decade. Cloud-based platforms, mobile applications, IoT sensors, and AI-powered analytics have become standard tools rather than competitive advantages. This proliferation of technology creates both opportunities and challenges.
Modern freight forwarders juggle dozens of systems daily: booking platforms, customs clearance tools, carrier portals, financial systems, and customer-facing applications. Without robust API integration, these systems remain isolated islands of information, forcing teams to manually reconcile data and leading to costly errors and delays.
| Traditional Logistics | API-Integrated Logistics |
| Manual data entry across systems | Automated data synchronization |
| Batch processing with delays | Real-time information exchange |
| Fragmented visibility | End-to-end transparency |
| Reactive problem-solving | Proactive issue prevention |
| High error rates | Automated validation and accuracy |
Common Integration Challenges in Logistics
Let’s be honest API integration in logistics isn’t always smooth sailing. The industry faces unique challenges that make integration more complex than in other sectors.
Legacy systems that were never designed to connect with modern platforms, inconsistent data formats across carriers and partners, varying API standards, and security concerns around sensitive shipment data all create integration headaches.
Many logistics providers also work with partners who have different technological maturity levels. Your integration strategy needs to accommodate everything from cutting-edge cloud platforms to older systems that might only support basic file transfers. This diversity requires flexibility and careful planning.
Core Principles of Successful API Integration
Choosing the Right API Architecture
Not all APIs are created equal, and selecting the appropriate architecture for your logistics operations is crucial. The architecture you choose impacts everything from performance and scalability to maintenance complexity and development speed.
REST vs SOAP vs GraphQL
REST (Representational State Transfer) has become the dominant standard in logistics API integration for good reason. Its simplicity, stateless nature, and use of standard HTTP methods make it ideal for most logistics applications. When you’re building integrations for shipment tracking, booking confirmation, or document exchange, REST APIs offer the perfect balance of simplicity and functionality.
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) still appears in enterprise logistics systems, particularly in established carrier networks and customs platforms. While more rigid and complex than REST, SOAP provides built-in security features and standardized error handling that some organizations require for compliance reasons.
GraphQL represents the newer wave of API technology, allowing clients to request exactly the data they need. For complex logistics dashboards that pull information from multiple sources, GraphQL can significantly reduce the number of API calls and improve performance.
Security-First Integration Approach
Logistics data is sensitive shipment details, customer information, pricing structures, and route optimization algorithms all represent valuable business assets. Your API integration strategy must prioritize security from day one, not as an afterthought.
Authentication and Authorization Best Practices
Implementing robust authentication mechanisms is non-negotiable. OAuth 2.0 has become the industry standard for API authentication, providing secure, token-based access without exposing credentials.
At Cargofive, we implement multi-layered security that includes API keys for service identification, OAuth tokens for user authentication, and role-based access control to ensure each system and user can only access appropriate data.
Encryption is equally critical. All API communications should use TLS 1.2 or higher to protect data in transit. For particularly sensitive information like customs documentation or financial transactions, consider implementing additional encryption layers for data at rest.
Planning Your Logistics API Integration Strategy
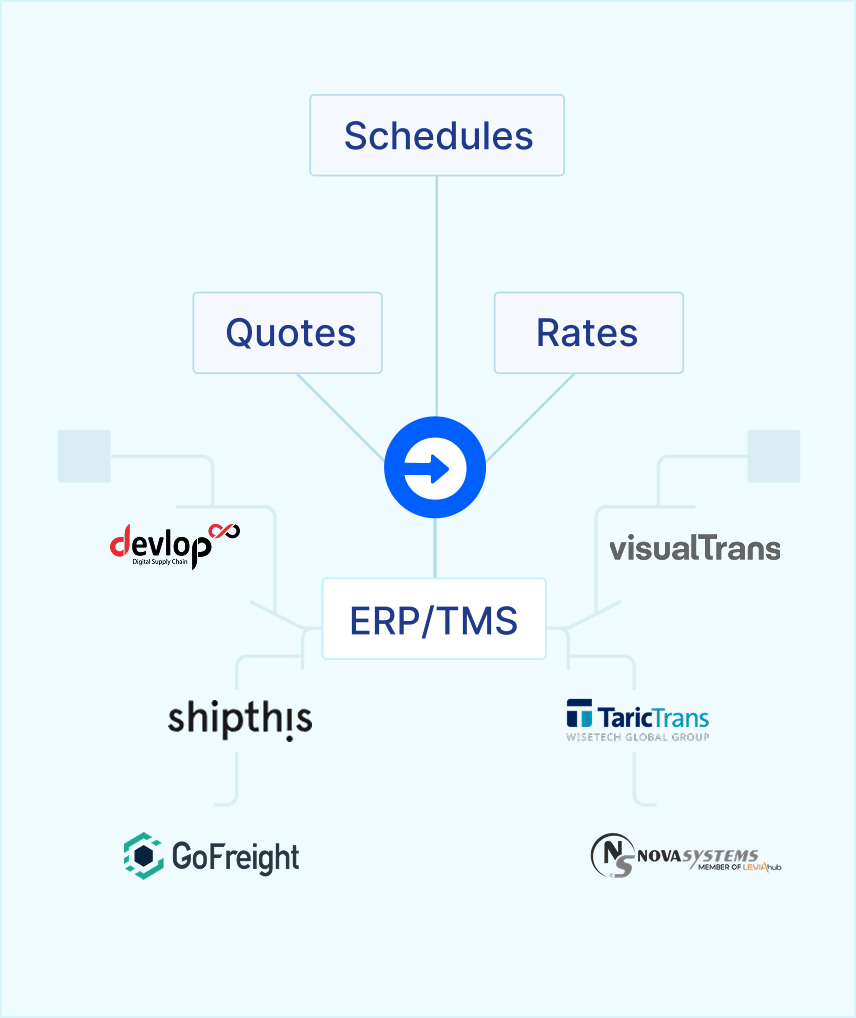
Identifying Integration Requirements
Before writing a single line of code or configuring any middleware, you need a crystal-clear understanding of what you’re trying to achieve. What business problems are you solving? Which systems need to communicate? What data needs to flow between them, and how frequently?
Start by mapping your current workflows. Where do bottlenecks occur? Where does manual data entry create delays or errors? These pain points often represent the highest-value integration opportunities.
At Cargofive, we prioritize integrations that directly impact customer experience and operational efficiency shipment visibility, automated status updates, and exception management typically deliver the most immediate value.
Mapping Data Flow Between Systems
Understanding data flow is like understanding traffic patterns in a busy port. You need to know what information moves where, when, and why. Create detailed data flow diagrams that document every integration point, including source systems, destination systems, data transformations, frequency of updates, and error handling procedures.

Consider data dependencies carefully. If System A needs data from System B before it can update System C, your integration architecture must account for this sequencing. Asynchronous processing, message queues, and event-driven architectures can help manage complex data flows while maintaining system performance and reliability.
Essential API Integration Best Practices
Implement Robust Error Handling
Here’s a truth bomb: your API integrations will fail. Networks drop, services go down, data formats change, and unexpected edge cases emerge. The question isn’t whether failures will occur it’s how gracefully your system handles them.
Implement comprehensive error handling that includes retry logic with exponential backoff, detailed error logging for troubleshooting, fallback mechanisms for critical functions, clear error messages for debugging, and automated alerts for integration failures.
Your error handling strategy should distinguish between temporary issues that warrant automatic retries and permanent failures that require human intervention.
Design for Scalability and Performance
Today you might process 100 shipments daily. Next year it could be 10,000. Your API integration architecture needs to scale without requiring complete redesigns. Use pagination for large data sets rather than attempting to retrieve everything in a single call.
Implement caching strategies for frequently accessed but rarely changed data. Consider rate limiting to prevent any single integration from overwhelming your systems.
Performance optimization isn’t just about speed it’s about resource efficiency. Optimize your API calls to request only necessary data fields. Use compression for large payloads. Implement asynchronous processing for operations that don’t require immediate responses. These practices ensure your integrations remain responsive even as volume grows.
Maintain Comprehensive Documentation
You know what’s worse than poorly documented APIs? APIs with no documentation at all. If you’re building APIs for partners or internal teams, comprehensive documentation isn’t optional it’s essential for adoption and proper usage.
Your API documentation should include endpoint descriptions with clear purposes, request and response examples, authentication requirements, rate limits and usage guidelines, error codes and troubleshooting guidance, and versioning information.
Tools like Swagger or OpenAPI Specification can automatically generate interactive documentation from your code, making it easier to keep documentation synchronized with your actual API implementation.
Version Control and API Lifecycle Management
APIs evolve. Requirements change, new features emerge, and occasionally you need to deprecate old functionality. How you manage these changes can mean the difference between smooth transitions and integration chaos.
Implement semantic versioning for your APIs. Major versions indicate breaking changes, minor versions add functionality in a backward-compatible manner, and patch versions represent backward-compatible bug fixes.

When you need to introduce breaking changes, maintain support for previous versions for a reasonable transition period typically at least six months giving integration partners time to update their implementations.
Real-World Implementation at Cargofive
How We Approach API Integrations
At Cargofive, we’ve built our entire platform around API-first principles. Every feature we develop is accessible through well-documented APIs, enabling seamless integration with customer systems, carrier networks, and partner platforms. Our approach emphasizes flexibility without sacrificing reliability.
We implement a hub-and-spoke integration model where Cargofive serves as the central hub connecting various logistics systems. This architecture reduces integration complexity for our customers instead of building separate connections to dozens of carriers and service providers, they integrate once with Cargofive and gain access to our entire network.
| Integration Layer | Function | Technology |
| API Gateway | Request routing, authentication, rate limiting | Cloud-based gateway services |
| Integration Layer | Data transformation, protocol translation | Middleware platforms |
| Business Logic | Shipment processing, rate calculation, tracking | Core application services |
| Data Layer | Persistent storage, caching | Database clusters and in-memory caches |
| External Connections | Carrier APIs, customs systems, partner platforms | Various protocols and standards |
Lessons Learned from the Field
Building and maintaining logistics API integrations has taught us valuable lessons. Start small and iterate rather than attempting massive integration projects upfront. We’ve found that launching with core functionality and gradually expanding capabilities leads to more stable, maintainable integrations than trying to build everything at once.
Partner communication is critical. When integrating with external systems, establish clear communication channels with technical contacts at partner organizations. Many integration issues stem from misunderstandings about data formats, timing expectations, or error handling procedures rather than actual technical problems.
Monitor everything. You can’t improve what you don’t measure. We instrument every API endpoint with detailed metrics covering response times, error rates, call volumes, and data quality indicators. This telemetry enables proactive problem detection and data-driven optimization decisions.
Testing and Quality Assurance
API Testing Strategies
Thorough testing separates reliable integrations from ticking time bombs. Your API testing strategy should encompass multiple layers, each addressing different aspects of integration quality.
Unit tests verify individual API endpoints function correctly in isolation. Integration tests confirm multiple systems work together properly. Load tests ensure your APIs handle expected traffic volumes. Security tests identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors do.
Don’t overlook edge case testing. What happens when someone sends malformed data? How does your system handle missing required fields? What occurs if an upstream service times out? Testing these scenarios in development prevents painful production incidents later.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Post-deployment monitoring is where many integration initiatives fall short. You need real-time visibility into API performance, error rates, and usage patterns. Implement comprehensive monitoring that tracks API response times, error frequency and types, data throughput, system resource utilization, and integration availability.
Set up automated alerting for anomalies. If error rates spike, response times degrade, or an integration stops processing data, you need to know immediately ideally before customers notice problems. At Cargofive, we use threshold-based alerts combined with anomaly detection algorithms to catch both obvious failures and subtle degradations.
Future Trends in Logistics API Integration

AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence is transforming logistics, and API integration makes these capabilities accessible throughout your technology stack.
Machine learning models can predict shipment delays, optimize routing, and forecast demand but only if they can access real-time data from across your systems.
The next generation of logistics APIs will increasingly incorporate AI-powered features: predictive ETAs that adjust based on real-time conditions, automated exception management that resolves issues before they escalate, intelligent document processing that extracts data from unstructured sources, and dynamic pricing APIs that optimize rates based on market conditions.
IoT and Real-Time Tracking APIs
The Internet of Things is bringing unprecedented visibility to logistics operations. Smart containers report temperature and location, sensor-equipped pallets track handling conditions, and connected vehicles provide real-time performance data. APIs are the conduit that transforms this IoT data into actionable insights.
Future logistics platforms will seamlessly integrate IoT data streams with traditional shipment management systems, creating comprehensive visibility across physical and digital supply chains.

This integration enables proactive interventions rerouting a temperature-sensitive shipment when sensors detect cooling failures, or alerting customers to delays before they impact operations.
Conclusion
API integration has evolved from a technical nicety to a business necessity in modern logistics. The companies thriving in today’s competitive landscape are those that have embraced integration as a strategic priority, connecting systems, partners, and customers into cohesive digital ecosystems.
The best practices outlined here security-first design, robust error handling, comprehensive documentation, scalable architecture, and continuous monitoring provide a roadmap for successful logistics API integration.
Whether you’re building your first integration or optimizing an existing architecture, these principles will guide you toward reliable, performant connections that drive business value.
At Cargofive, we’re committed to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with logistics API integration.
By following these best practices and staying attuned to emerging trends, we’re building the connected, intelligent supply chain platform that modern businesses demand.
Remember: great API integration isn’t about using the fanciest technology or the most complex architecture.
It’s about creating reliable connections that solve real business problems, deliver value to customers, and adapt as your needs evolve. Start with solid fundamentals, iterate based on real-world feedback, and never stop improving.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What’s the difference between API integration and EDI in logistics?
API integration provides real-time, bidirectional data exchange using modern web technologies, while EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) relies on structured document exchange with batch processing. APIs offer greater flexibility, faster implementation, and better support for mobile and web applications. However, EDI remains important in logistics as many established carriers and partners still use it. The best approach often involves supporting both methods depending on partner capabilities.
How long does it typically take to implement a logistics API integration?
The timeline varies significantly based on integration complexity, system maturity, and available resources. Simple integrations connecting two modern REST APIs might take 2-4 weeks, while complex multi-system integrations involving legacy platforms could require 3-6 months. At Cargofive, we prioritize rapid integration by providing comprehensive documentation, sandbox environments, and technical support that accelerates implementation timelines for our partners.
What security measures are most critical for logistics API integrations?
The three most critical security measures are authentication and authorization using industry standards like OAuth 2.0, encryption for all data in transit using TLS 1.2 or higher, and comprehensive logging and monitoring to detect suspicious activity. Additionally, implement rate limiting to prevent abuse, validate all input data to prevent injection attacks, and regularly update dependencies to patch known vulnerabilities.
Should we build custom integrations or use integration platforms?
This depends on your integration volume and complexity. For a few strategic integrations with custom requirements, building directly might make sense. However, most organizations benefit from integration platforms or middleware solutions that provide pre-built connectors, data transformation tools, and monitoring capabilities. These platforms reduce development time, simplify maintenance, and provide scalability as your integration needs grow.
How do we handle API versioning when updating logistics integrations?
Implement semantic versioning and maintain backward compatibility whenever possible. When breaking changes are necessary, release them as new major versions while continuing to support previous versions for a defined transition period (typically 6-12 months). Communicate changes clearly to integration partners well in advance, provide migration guides with code examples, and offer a deprecation timeline that gives partners adequate time to update their implementations without disrupting operations.
AUTHOR



